- Home
- Blog
- Plastic Polymer Composite Article
- A Comparative Study of PVC Compound and Masterbatch: Key Materials in Plastics Processing
A Comparative Study of PVC Compound and Masterbatch: Key Materials in Plastics Processing

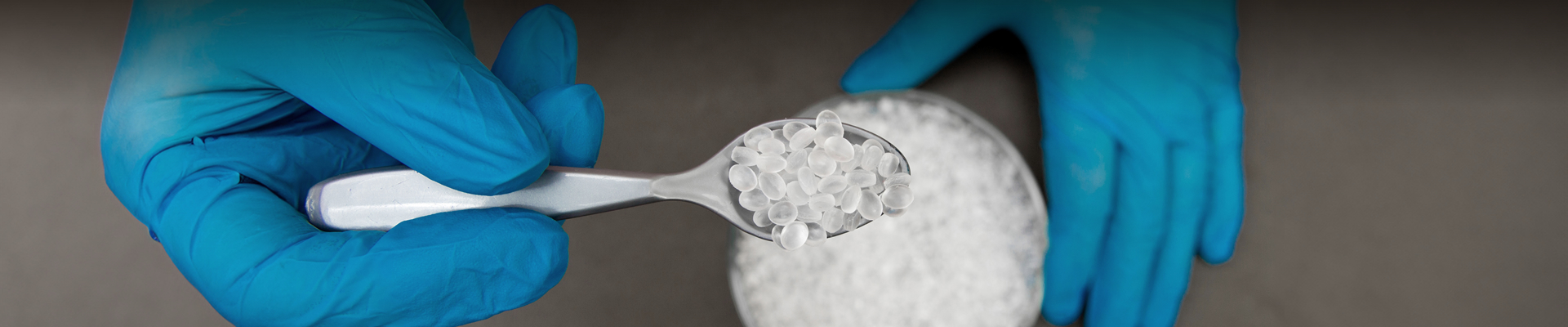
In the plastic manufacturing and processing industry, PVC Compounds and Masterbatch are important materials. These two materials are widely used in various fields, including cables, construction materials, and plastic piping, but they differ in characteristics and applications. This article will delve into the features, manufacturing processes, and uses of PVC Compound and Masterbatch, helping you better understand and choose between these two crucial materials.
Introduction to PVC Compound
PVC Compound is a pre-mixed plastic composite material, which is made of PVC resin combined with various additives according to a specific formula. These additives may include plasticizers, stabilizers, fillers, lubricants, pigments, etc. PVC Compound is a finished formula that can be directly processed into final products without the need for further mixing with other materials.
〈Recommended Product:PVC Compound〉
Types of PVC Compound
- Rigid PVC Compound: Used for manufacturing pipes, and window profiles, etc.
- Flexible PVC Compound: Applied in cable sheathing, flooring, etc.
- Semi-rigid PVC Compound: A blend between rigid and flexible and is used for specialized applications.
PVC Compound Process
The manufacturing process of PVC Compound usually includes the following steps:
1. Raw material mixing and melting steps
The primary plastic powder is mixed with other additives in specified proportions. Usually, 85-95% plastic powder, 0.1-10% light diffusion powder, and 2-14.5% anti-blue light powder are blended evenly using a mixer and then heated to a certain temperature to ensure the materials are fully mixed and plasticized.
2. Cooling and Solidification step
The fully or partially melted plastic mixture is extruded into the desired shape through a screw. The extrudate is then cooled to a solidification temperature using water or air cooling methods, such as blowers, to solidify it into a dry solid form.
3. Pelletizing Process steps
The solidified plastic strands are cut using a pelletizer, precisely trimmed to the required pellet size depending on their intended use. The final product appears as blocks or granules, completing the PVC Compound manufacturing process.
Application fields of PVC Compound
PVC Compound typically appears in granular or pellet form, making it easy to process and use for producing both soft and rigid PVC parts, such as pipes, sheets, and films. Below are six major industries where PVC Compound is applied:
1. Cable Trunking industry
- Improve insulation: Ensure safe operation of wires
- Increases wear and weather resistance: Extends product lifespan.
- Improve processing performance: Facilitate the production of wire ducts of various shapes and sizes
- Improve product quality: Boosts overall performance and durability.
2. PVC Flooring Industry
- Enhanced weather resistance, impact resistance and abrasion resistance: reduce aging, fading and surface damage
- Adjust hardness and softness: Accommodates different process requirements
- Improved impact and scratch resistance: Extends the product’s lifespan.
- Achieve diverse colors and appearances: Enhance product appeal
3. Window frame industry
- Reduce production costs: Improve market competitiveness
- Enhance tensile strength and weather resistance: Improve product durability
- Minimizes deformation and wear: extend service life
- Provides a variety of color choices: Enhance the aesthetics of the building
- Improve sound insulation and thermal insulation performance: Increases window frame functionality
4. Plastic valve industry
- Improve material flow and processability: Facilitate the manufacture of valves of various shapes and sizes
- Enhanced durability: Improved oxidation resistance, weather resistance and chemical stability
- Reduce production costs: Increases efficiency, saving raw materials and energy
5. Optical Fiber Cable Applications
- Produces protective sleeves: Moisture-proof, corrosion-resistant, ensuring fiber stability.
- Enhanced flame retardancy: Improved safety
- Improve mechanical properties: Boosts tensile strength and wear resistance, reducing damage rate
- Provides diversified appearance: Meet different product needs
6. Plastic pipes and plates
- Enhances processing performance: Increase flow, facilitate molding, cutting and installation
- Enhanced UV resistance: Especially suitable for transparent PVC pipes maintaining transparency
- Improve physical properties: Increase strength, hardness, tensile strength, compressive strength and wear resistance
- Adapts to a various of products: Suitable for pipes, plates, transparent plastic pipes and other products
Introduction to Masterbatch
Masterbatch is a high-concentration additive carrier mainly used in the plastic processing industry. It is a granular mixture where pigments, fillers, or other additives are highly concentrated and dispersed within a resin carrier. The purpose of masterbatch is to provide color or specific functionality during the plastic processing stage, simplifying production processes and enhancing product quality.
〈Recommended Products:Calcium Carbonate Masterbatch、Ultra-fine Ground Calcium Carbonate〉
Features of Masterbatch
- High Concentration: Typically contains 20-80% additives, much higher than the concentration in the final product.
- Easy Dispersion: Designed to ensure quick and uniform dispersion of additives within the base resin.
- Versatility: Provide color and functional properties, such as UV stability, flame retardant, etc.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduce the number of SKU in inventory and production costs.
- Precise Control: Allows for accurate control of additive quantities.
Types of masterbatch
1. Masterbatch
The most common type, used for coloring plastics.
- Single-Color Masterbatch: Contains a single color pigment
- Multi-Color Masterbatch: Includes multiple pigments for special color effects.
2. White Masterbatch
Contains high concentrations of white pigments (e.g., titanium dioxide), to increase the opacity and brightness in plastics.
3. Black Masterbatch
Contains carbon black pigment and is used to produce black plastic products.
4. Functional Masterbatch
- Antistatic Masterbatch: Reduce static accumulation on plastic surfaces.
- Antibacterial Masterbatch: Provides antibacterial properties, commonly used in medical and food packaging.
- Flame Retardant Masterbatch: Improves the flame retardant performance of plastic products.
- UV Stabilizer Masterbatch: Enhance the resistance to UV radiation, extending outdoor durability.
- Foaming Masterbatch: Used for producing lightweight foam plastic products.
5. Filler Masterbatch
Contains mineral fillers (e.g., calcium carbonate, talc powder, etc.), used to improve the mechanical properties of plastics or reduce costs.
Masterbatch manufacturing process
- Ingredients Preparation: Precise weighing of various raw materials according to the formula.
- Pre-Mixing: Initial mixing of pigments or additives with part of the resin carrier.
- Melting and mixing: Melting the mixture at high temperatures, followed by dispersion and homogenization.
- Extrusion: Extruding the molten mixture through an extruder.
- Cooling: Cooling and solidifying the extruded material.
- Pelletizing: Cutting the cooled material into uniform granules.
- Screening and packaging: Quality inspection, screening of qualified products, and packaging.
Application areas of Masterbatch
- Packaging industry: Plastic bags, food containers, beverage bottles, etc.
- Automobile industry: Interior parts, dashboards, exterior parts, etc.
- Electronic appliances: Household appliance casings, electronic product accessories, etc.
- Construction industry: Pipes, profiles, doors and windows, etc.
- Agriculture: Agricultural film, irrigation system, etc.
- Consumer goods: Toys, household items, sports equipment, etc.
- Medical industry: Medical equipment, pharmaceutical packaging, etc.
Comparison of PVC Compound and Masterbatch
Composition
- PVC Compound: Contains base PVC resin and all necessary additives, a complete formula.
- Masterbatch: Typically contains a high concentration of pigments or functional additives and needs to be mixed with the base resin during use. Primarily used to provide color or specific functions.
Usage
- PVC Compound: Ready for directly for molding processing without additional mixing steps. Ideal for situations where quick production or the absence of mixing equipment is needed.
- Masterbatch: Requires blending with base resin in a specific ratio before use. This process requires an additional mixing step during production but allows for more precise control over the formulation.
Concentration
- PVC Compound: Lower concentration of additives, typically between 10-40%, suitable for direct processing without further dilution.
- Masterbatch: High additive concentration, ranging from 20-80%. The high concentration means less material is needed, saving on transportation and storage costs, but requires precise mixing with the base resin.
Flexibility
- PVC Compound: Fixed formula, low flexibility. Each Compound has specific properties and colors, and changing the formulation requires reordering a different recipe.
- Masterbatch: Allows for the adjustment of additive ratios according to needs, offering higher flexibility. This is suitable for production scenarios where product characteristics need to be frequently changed.
How to choose: PVC Compound or Masterbatch?
The choice between PVC Compound and Masterbatch depends on various factors, including your specific needs, production scale, technical capabilities, and cost considerations. Here’s a detailed guide to help you decide:
When choosing PVC Compound
- Direct Usage requirements: If you need a material ready for immediate molding and processing, PVC Compound is ideal. It contains all the necessary additives, requiring no additional mixing.
- Large-Scale Production: For large-scale production, using PVC Compound can simplifies the production process and increases efficiency.
- High stability requirements: If your product has strict performance stability, pre-formulated PVC Compound can provide more consistent quality.
- Limited Expertise: If your team has limited experience with recipe adjustments, using ready-made PVC Compound reduces the risk of errors. APEX offers a professional R&D team that can customize PVC Compound according to your needs.
- Special Performance Requirements: Some specific performance (e.g., high flame resistance, high weatherability) PVC products may require complex formulations, making it more appropriate to choose professionally formulated PVC Compound.
When choosing Masterbatch
- Flexibility Requirement: If you frequently need to adjust the color or functional properties of your products, Masterbatch provides greater flexibility.
- Inventory Management: Using Masterbatch can reduce the number of SKUs stock as you can manufacture a variety of products using the same base resin with different Masterbatches.
- Cost-effectiveness: For small batches or multi-variety production, using Masterbatch may be more cost-effective because you can adjust the addition ratio according to your needs.
- Customized Requirements: If your customers often request specific colors or functions, using Masterbatch can respond to these requirements more quickly.
- Strong Technical Capability: If your team has expertise in blending and mixing, using Masterbatch can give you more control and achieve more precise performance adjustments.
- Space Saving: Masterbatch is usually more concentrated than PVC Compound, saving storage space.
Comprehensive Considerations
- Product type: Some products may be better suited to PVC Compound (such as medical supplies requiring high consistency), while others may be better for Masterbatch (such as consumer goods with frequently changing colors).
- Production Equipment: Make sure your equipment can effectively handle the materials you choose. Using Masterbatch may require additional mixing equipment.
- Quality Control: Consider your quality control capabilities. Using PVC Compound may be easier to maintain consistent quality, while using Masterbatch requires more rigorous process control.
- Environmental Factors: In some cases, using Masterbatch may be more environmentally friendly because it reduces material waste.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Evaluate the reliability and lead time of suppliers. Sometimes, choices may be influenced by supply chain factors.
FAQ
Q1: How to ensure the quality of PVC Compound products?
To ensure the quality of PVC Compound products, the key is to have a complete quality control system. A high-quality supplier will provide professional in-factory quality control inspection, usually covering four stages: incoming material sampling inspection, in-process quality control inspection, finished product quality inspection, and post-production analytical inspection. These stages enable comprehensive monitoring of the product production process to ensure that the PVC Compound produced meets high standards of quality.
Q2: What international standard should a high-quality PVC Compound pass?
A high-quality PVC Compound should pass multiple international standard tests. In addition to in-factory quality inspection, institutional inspection is equally important! This includes testing items to ensure that plastic Masterbatch meets international standards, such as RoHS specifications, eight heavy metal testing, powder inspection, tensile testing, etc., and follows relevant standards such as IEC 62321:2008, EN71-3, ASTM-F963, etc. These standards ensure the safety and quality of PVC Compound.
APEX's PVC Compound Features
- Premium Raw Materials: We use high-quality PVC resin as the base material to ensure the stability and reliability of the product.
- Highly Customizable: We offer a wide range of color options and custom formulas to meet customer-specific application needs.
- Superior Coloring Performance: Our PVC Compound exhibits excellent coloring performance, which can achieve uniform and stable color distribution in plastic products and improve their visual appeal.
- Modification function: In addition to coloring, our PVC Compound has modification capabilities that improve the mechanical properties, weather resistance, and overall quality of plastic products.
- Environmentally Friendly and Reliable: Our products can be customized to comply with relevant environmental standards to ensure safe and reliable use.
- Stability and Reliability: Through strict quality control and testing processes, we ensure the stability and reliability of each batch of products.
- Wide range of applications: Our PVC Compound is widely used in optical fiber, wire insulation and sheathing, rigid extrusion, rigid injection molding, flexible extrusion and flexible injection molding to meet different application needs.
- Customizable: Our products can be customized according to customers' specific requirements to ensure that the products fully meet customer needs.
Conclusion
PVC Compound and Masterbatch are both important materials in plastic processing, each with its own unique characteristics and application. Understanding the differences and applications of these two materials can help you make the right choice for different production needs. As a professional supplier, APEX provides high-quality PVC Compound and Masterbatch products to meet customer needs in various fields. No matter which material you choose, APEX can provide you with a professional solution. Feel free to contact us .
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- What is limestone powder? Applications of limestone powder
- What is filler masterbatch resin? How is it applied?
- Top 10 types of plastics used in injection molding technology
- What are fillers? Classification and applications of plastic fillers
- What are plastic additives? 11+ common types of plastic additives