BLOG
- Home
- Blog
- Plastic Polymer Composite Article
- Top 10 types of plastics used in injection molding technology
Top 10 types of plastics used in injection molding technology

What is plastic injection molding?It is one of the most common and efficient plastic processing technologies today, widely used to manufacture consumer goods, technical equipment, and industrial components. To ensure product quality and optimize production processes, selecting the right materials is extremely important. So, which types of plastics are used for injection molding, what are their properties, and how are they applied in practice? Let’s explore these questions with VNAPEX in the detailed summary below.
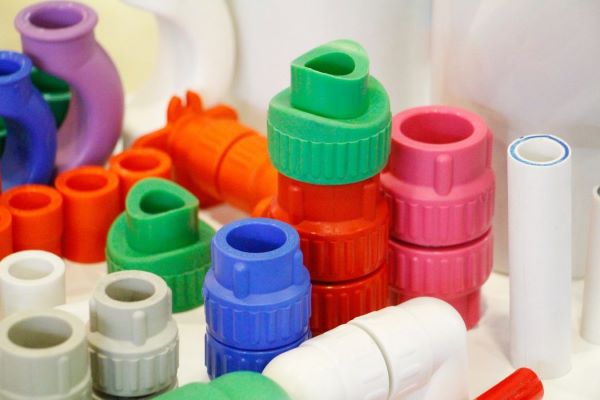

Plastic injection molding process and modern injection molding machines applying CNC in production
What is plastic injection ?
Injection molding is a shaping technique that uses a mold, in which materials such as synthetic plastics are melted and then injected into the mold under high pressure. When the material cools and solidifies, it forms a product with the desired shape. This method is called injection molding because its operation is similar to injecting a liquid using a syringe.
Plastic injection molding process and modern injection molding machines applying CNC in production
The injection molding process takes place through the following steps: melting the material, injecting it into the mold, cooling it down, and then removing the finished product from the mold.
Currently, injection molding machines are divided into three main types:
Although polyethylene has many advantages, it is not suitable for products that need high heat resistance because of its temperature limit. However, with its light weight, strength, and easy processing, polyethylene used in injection molding is widely applied in making household goods, toys, food containers, and car parts.
Polyethylene (PE) Injection Molding
Although polypropylene has many advantages, it also has some limitations. This material catches fire easily, is sensitive to UV rays, and can break down at temperatures above 100°C, creating harmful aromatic hydrocarbons. In addition, the surface of PP is hard to paint and bond, which can be a problem during some finishing processes.
Polypropylene is widely used in many fields such as toys, containers, sports equipment, packaging, machine parts, and handheld electrical devices.
Polypropylene (PP) Injection Molding
In addition, this polymer can resist gamma radiation and has good chemical resistance to dilute acids and bases. Because of this, it is often used for sterilizing medical equipment
Polystyrene is used in many fields such as medical, optical, electrical, and electronic industries. With good impact strength, HIPS is often used for machine and device casings. Meanwhile, injection-molded GPPS is suitable for producing plastic trays, containers, and toys. However, both types have weaknesses they are flammable and can degrade under ultraviolet (UV) light.
ABS is known for its strong mechanical properties and high impact resistance. However, this material is not very durable when exposed to sunlight, moisture, or harsh weather conditions for a long time. Compared to acrylic, injection-molded ABS is not the best choice for outdoor use.
In practice, injection-molded ABS is widely used in the production of computer keyboards, safety helmets, electrical switch covers, control panels, wheel covers, and many parts in the automotive industry.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) plastic injection molding
The flexible adaptability of PVC material to various molding techniques not only helps optimize the production process but also expands its applications across multiple industries, from construction and electrical–electronic to medical and packaging. Thanks to these outstanding properties, PVC has maintained its position as one of the most preferred materials in the market.
Although it is not highly resistant to scratches, PC is much tougher and stronger than glass, making it an ideal choice for applications that require both durability and optical clarity. In particular, this material maintains color well when dyed and offers excellent light transmission, making it suitable for various lighting and display applications.
Polycarbonate is commonly used to produce machine guards, transparent or colored windows, light diffusers, and light guides for LED lamps. In addition, it is also well-suited for making clear molds in silicone and urethane casting processes.
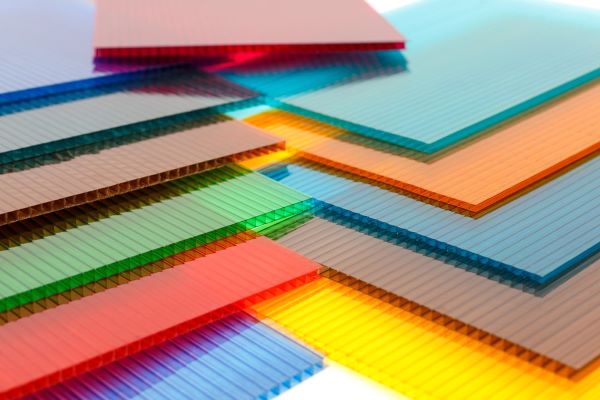

Polycarbonate (PC) Injection Molding
This type of plastic is widely used in the production of beverage bottles, food packaging, and textile products such as polyester fabrics. Its high recyclability makes PET an environmentally friendly choice for modern consumer applications.
In the injection molding process, acrylic allows for tight tolerances, providing high precision for finished products. However, this material is not chemical-resistant, as it can be affected by grease and oil and tends to absorb odors. Although it has good tensile strength, acrylic is prone to stress cracking when exposed to heavy or prolonged mechanical loads.
Acrylic is widely used in products that require high transparency and aesthetic appeal, such as windows, greenhouses, solar panels, shower partitions, and transparent components for architecture, lighting, and outdoor design.
Nylon is widely used in industries that require durability and stable mechanical performance, such as precision engineering, automotive, electrical and electronic manufacturing, and high-end consumer goods. Its excellent adaptability to various processing methods makes nylon a preferred choice in many modern production processes.
Nylon (Polyamide, PA) injection molding
The company specializes in supplying Taical filler masterbatch, which uses ultra-fine calcium carbonate powder (1.8–3.3 μm) with a filler content of up to 75–88% in PP and PE base products. These products help to:
Understanding what plastic injection molding is and choosing the right suitable materials will help optimize production efficiency, improve product quality, and reduce costs during the processing. With the diversity of plastics used in injection molding technology, each type offers its own advantages, suitable for different applications and technical requirements. Mastering the characteristics of each type of plastic is the key to successfully applying injection molding technology in practice.
Currently, injection molding machines are divided into three main types:
- Mechanical machines using servo motors.
- Hydraulic machines operated by hydraulic motors.
- Hybrid machines that combine both servo motors and hydraulic motors to optimize performance.
Common Types of Plastics Used in Injection Molding
In the field of engineering plastics and thermoplastics, each material has its own unique properties, meeting different requirements in terms of mechanical strength, optical clarity, chemical resistance, and applications. Below is an overview of the most common types of plastics used in injection molding, along with their key characteristics and typical applications.Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is the most widely used plastic in the world and one of the main commercial polymers that can be classified based on its density. The two main types High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) both offer excellent chemical resistance but differ in rigidity, flexibility, melting point, and optical transparency.Although polyethylene has many advantages, it is not suitable for products that need high heat resistance because of its temperature limit. However, with its light weight, strength, and easy processing, polyethylene used in injection molding is widely applied in making household goods, toys, food containers, and car parts.

Polyethylene (PE) Injection Molding
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is the second most widely used plastic in the world. It has a high melting point and strong resistance to chemicals. One special feature of PP is that it can keep its shape after being bent or twisted, and it is not affected by water or moisture. In production, injection-molded polypropylene is a recyclable material used in many industries.Although polypropylene has many advantages, it also has some limitations. This material catches fire easily, is sensitive to UV rays, and can break down at temperatures above 100°C, creating harmful aromatic hydrocarbons. In addition, the surface of PP is hard to paint and bond, which can be a problem during some finishing processes.
Polypropylene is widely used in many fields such as toys, containers, sports equipment, packaging, machine parts, and handheld electrical devices.

Polypropylene (PP) Injection Molding
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is a light and inexpensive type of plastic. It can resist moisture and help stop bacteria from growing. The two main types are General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) and High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS).In addition, this polymer can resist gamma radiation and has good chemical resistance to dilute acids and bases. Because of this, it is often used for sterilizing medical equipment
Polystyrene is used in many fields such as medical, optical, electrical, and electronic industries. With good impact strength, HIPS is often used for machine and device casings. Meanwhile, injection-molded GPPS is suitable for producing plastic trays, containers, and toys. However, both types have weaknesses they are flammable and can degrade under ultraviolet (UV) light.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is an engineering plastic with a low melting point, making the molding process easier and more efficient. This opaque polymer is also very flexible in coloring, surface treatment, and creating different textures according to design requirements.ABS is known for its strong mechanical properties and high impact resistance. However, this material is not very durable when exposed to sunlight, moisture, or harsh weather conditions for a long time. Compared to acrylic, injection-molded ABS is not the best choice for outdoor use.
In practice, injection-molded ABS is widely used in the production of computer keyboards, safety helmets, electrical switch covers, control panels, wheel covers, and many parts in the automotive industry.

Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) plastic injection molding
Polyvinyl Clorua (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most common thermoplastics and is widely used in injection molding technology thanks to its flexibility, high durability, and cost efficiency. With excellent chemical resistance, moisture protection, and impact strength, PVC is an ideal choice for a variety of products, from water pipes and fittings to consumer goods.The flexible adaptability of PVC material to various molding techniques not only helps optimize the production process but also expands its applications across multiple industries, from construction and electrical–electronic to medical and packaging. Thanks to these outstanding properties, PVC has maintained its position as one of the most preferred materials in the market.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a lightweight and durable material with high natural transparency and stable physical properties across a wide temperature range. Thanks to its uniform and predictable shrinkage, polycarbonate allows for precise dimensional control and tight tolerances during the injection molding process.Although it is not highly resistant to scratches, PC is much tougher and stronger than glass, making it an ideal choice for applications that require both durability and optical clarity. In particular, this material maintains color well when dyed and offers excellent light transmission, making it suitable for various lighting and display applications.
Polycarbonate is commonly used to produce machine guards, transparent or colored windows, light diffusers, and light guides for LED lamps. In addition, it is also well-suited for making clear molds in silicone and urethane casting processes.

Polycarbonate (PC) Injection Molding
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a strong, lightweight plastic with excellent chemical resistance. It is highly valued for its safety, mechanical strength, and easy recyclability. With its transparency and effective gas barrier properties, PET is an ideal material for packaging applications.This type of plastic is widely used in the production of beverage bottles, food packaging, and textile products such as polyester fabrics. Its high recyclability makes PET an environmentally friendly choice for modern consumer applications.
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic (PMMA – Polymethyl Methacrylate) is a transparent thermoplastic that is strong, durable, and more shatter-resistant than glass. It also offers excellent light transmission, allowing light to pass through with high clarity. Unlike many other polymers, acrylic is water-resistant and maintains its properties without degradation.In the injection molding process, acrylic allows for tight tolerances, providing high precision for finished products. However, this material is not chemical-resistant, as it can be affected by grease and oil and tends to absorb odors. Although it has good tensile strength, acrylic is prone to stress cracking when exposed to heavy or prolonged mechanical loads.
Acrylic is widely used in products that require high transparency and aesthetic appeal, such as windows, greenhouses, solar panels, shower partitions, and transparent components for architecture, lighting, and outdoor design.
Nylon (Polyamide, PA)
Nylon (Polyamide, PA) is a common thermoplastic that is highly valued for its excellent mechanical strength, good wear resistance, and strong chemical resistance. With its toughness, durability, and stability under harsh conditions, nylon is an ideal material for high-performance engineering applications.Nylon is widely used in industries that require durability and stable mechanical performance, such as precision engineering, automotive, electrical and electronic manufacturing, and high-end consumer goods. Its excellent adaptability to various processing methods makes nylon a preferred choice in many modern production processes.

Nylon (Polyamide, PA) injection molding
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyoxymethylene (POM), commonly known as acetal, is a high-performance engineering plastic that stands out for its low friction coefficient, excellent stiffness, and good thermal stability. Naturally opaque white in color, POM is divided into two main types: homopolymer, which offers higher stiffness and tensile strength, and copolymer, which provides better thermal and chemical stability.
Thanks to its excellent mechanical properties, injection-molded POM is widely used in moving components such as bearings, gears, conveyor belts, and pulleys. In addition, this material is also applied in mechanical pins, eyeglass frames, knife and firearm parts, locking systems, and other high-performance engineering components, due to its durability and precision in demanding operating environments.
Leading Supplier of Filler Masterbatch in the Plastics Industry
APEX MATERIAL INDUSTRIAL VIETNAM CO., LTD (VN APEX), a strategic member of TW APEX Taiwan since 2018, is a trusted destination for plastics businesses in Southeast Asia. With over 50 years of experience in raw materials such as calcium carbonate and various filler masterbatches, VN APEX has established an automated production system meeting international standards, while strictly complying with high environmental and quality requirements.The company specializes in supplying Taical filler masterbatch, which uses ultra-fine calcium carbonate powder (1.8–3.3 μm) with a filler content of up to 75–88% in PP and PE base products. These products help to:
- Increase stiffness, compressive strength, and wear resistance, ensuring high mechanical performance.
- Reduced shrinkage, good size control and reduced plastic raw material costs.
- Suitable for injection molding, extrusion, spinning and application in agricultural film, plastic pipes, plastic sheets, household and automotive parts.
Understanding what plastic injection molding is and choosing the right suitable materials will help optimize production efficiency, improve product quality, and reduce costs during the processing. With the diversity of plastics used in injection molding technology, each type offers its own advantages, suitable for different applications and technical requirements. Mastering the characteristics of each type of plastic is the key to successfully applying injection molding technology in practice.
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- What is limestone powder? Applications of limestone powder
- What is filler masterbatch resin? How is it applied?
- Top 10 types of plastics used in injection molding technology
- What are fillers? Classification and applications of plastic fillers
- What are plastic additives? 11+ common types of plastic additives